Animatics (SmartMotor series) Protocol v 1.00
See also: Help for Serial Protocols
Overview
The Animatics serial downloadable protocol is for communication between the Animatics SmartMotor drives and an OCS. This is a Master/Slave protocol.
CSCAPE Configuration
To configure the OCS for the Animatics SmartMotor protocol, select the Protocol Configuration from the Program menu in CSCAPE software. Select the appropriate protocol type on the desired port. To make sure that the Software is able to configure the equipment for the correct protocol, make sure the Animatics.dll file is in Protocols directory of the current working/open Cscape.
Protocol Revisions
Animatics SmartMotor Protocol supports master communications to the slave using ASCII commands.
Serial Port Format
The default link settings are : 9600 baud, No parity, Eight data bits, No handshaking and RS232 Communications mode.
Communications in 232 mode is via the 7 way male D-sub port located on the top of the motor and the selected port.
Station Node Address
The station node address for the drive is default to 0 unless changed via the SADDR or ADDR= commands. If there is more than 1 motor on the bus, access is different. Sending 0x80 (0 in decimal) prior to the command will send the selected command to all motors on the bus (default on power up of drive). To specifically address one motor, send the specific address of the required motor before sending the command.
Commands
Each motor parameter is accessed as a command as described in the following section. When these commands are being accessed in CSCAPE the name of each command may be directly used.
Note: Every command must be configured as a 32-bit memory location for accessibility reasons i.e. even if the command is 8-bit, 16-bit or 32-bit the register must be given 32-bit of memory space. So if %R1 contains one command, %R3 should be used not %R2 for the next command.
ECHO Command
On boot up of the OCS devices, the ECHO is set to ECHO_OFF. This is because on boot up the device does not know what the drive is set to. So to make sure the echo is on, ECHO_ON command must be set.
|
Address |
Name |
Address |
Name |
Address |
Name |
Address |
Name |
Address |
Name |
|
0 |
@P |
55 |
aaa |
110 |
BRKG |
165 |
MF1 |
220 |
UAO |
|
1 |
@PE |
56 |
bbb |
111 |
BRKI |
166 |
MF2 |
221 |
UB |
|
2 |
@V |
57 |
ccc |
112 |
BRKRLS |
167 |
MF4 |
222 |
UBA |
|
3 |
a |
58 |
ddd |
113 |
BRKSRV |
168 |
MFDIV |
223 |
UBI |
|
4 |
b |
59 |
eee |
114 |
BRKTRJ |
169 |
MFMUL |
224 |
UBO |
|
5 |
c |
60 |
fff |
115 |
CCHN |
170 |
MFR |
225 |
UC |
|
6 |
d |
61 |
ggg |
116 |
CHN0 |
171 |
MP |
226 |
UCA |
|
7 |
e |
62 |
hhh |
117 |
CHN1 |
172 |
MS |
227 |
UCI |
|
8 |
f |
63 |
iii |
118 |
CLK |
173 |
MS0 |
228 |
UCO |
|
9 |
g |
64 |
jjj |
119 |
CTR |
174 |
MSR |
229 |
UCP |
|
10 |
h |
65 |
kkk |
120 |
D |
175 |
MT |
230 |
UD |
|
11 |
i |
66 |
lll |
121 |
E |
176 |
MV |
231 |
UDA |
|
12 |
j |
67 |
mmm |
122 |
ECHO |
177 |
MTB |
232 |
UDI |
|
13 |
k |
68 |
nnn |
123 |
ECHO_OFF |
178 |
O |
233 |
UDM |
|
14 |
l |
69 |
ooo |
124 |
ECHO1 |
179 |
OCHN |
234 |
UDO |
|
15 |
m |
70 |
ppp |
125 |
ECHO1_OFF |
180 |
OFF |
235 |
UE |
|
16 |
n |
71 |
qqq |
126 |
ENC0 |
181 |
P |
236 |
UEA |
|
17 |
o |
72 |
rrr |
127 |
ENC1 |
182 |
PID1 |
237 |
UEI |
|
18 |
p |
73 |
sss |
128 |
EPTR |
183 |
PID2 |
238 |
UEO |
|
19 |
q |
74 |
ttt |
129 |
ES400 |
184 |
PID4 |
239 |
UF |
|
20 |
r |
75 |
uuu |
130 |
ES1000 |
185 |
PID8 |
240 |
UFA |
|
21 |
s |
76 |
vvv |
131 |
F |
186 |
|
241 |
UFI |
|
22 |
t |
77 |
www |
132 |
F=1 |
187 |
PRINT1 |
242 |
UFO |
|
23 |
u |
78 |
xxx |
133 |
F=4 |
188 |
Q |
243 |
UG |
|
24 |
v |
79 |
yyy |
134 |
F=8 |
189 |
RCHN |
244 |
UGA |
|
25 |
w |
80 |
zzz |
135 |
F=32 |
190 |
RCS |
245 |
UGI |
|
26 |
x |
81 |
al |
136 |
F=64 |
191 |
RCS1 |
246 |
UGO |
|
27 |
y |
82 |
aw |
137 |
G |
192 |
RES |
247 |
UIA |
|
28 |
z |
83 |
ab |
138 |
GETCHR |
193 |
RMODE |
248 |
UJA |
|
29 |
aa |
84 |
A |
139 |
GETCHR1 |
194 |
RPE |
249 |
UP |
|
30 |
bb |
85 |
ADDR |
140 |
I |
195 |
RPW |
250 |
UPLOAD |
|
31 |
cc |
86 |
AMPS |
141 |
KA |
196 |
RS |
251 |
V |
|
32 |
dd |
87 |
Ba |
142 |
KD |
197 |
RW |
252 |
VLD |
|
33 |
ee |
88 |
Bb |
143 |
KG |
198 |
S |
253 |
VST |
|
34 |
ff |
89 |
Bc |
144 |
KGOFF |
199 |
SADDR |
254 |
WAKE |
|
35 |
gg |
90 |
DBd |
145 |
KGON |
200 |
SILENT |
255 |
WAKE1 |
|
36 |
hh |
91 |
Be |
146 |
KI |
201 |
SILENT1 |
256 |
X |
|
37 |
ii |
92 |
Bf |
147 |
KL |
202 |
SIZE |
257 |
Z |
|
38 |
jj |
93 |
Bi |
148 |
KP |
203 |
SLD |
258 |
Za |
|
39 |
kk |
94 |
Bk |
149 |
KS |
204 |
SLE |
259 |
Zb |
|
40 |
ll |
95 |
Bl |
150 |
KV |
205 |
SLEEP |
260 |
Zc |
|
41 |
mm |
96 |
Bm |
151 |
LEN |
206 |
SLEEP1 |
261 |
Zd |
|
42 |
nn |
97 |
Bo |
152 |
LEN1 |
207 |
SLD |
262 |
Zf |
|
43 |
oo |
98 |
Bn |
153 |
LIMD |
208 |
SLP |
263 |
Zl |
|
44 |
pp |
99 |
Bp |
154 |
LIMH |
209 |
STACK |
264 |
Zr |
|
45 |
|
100 |
Br |
155 |
LIML |
210 |
T |
265 |
Zs |
|
46 |
rr |
101 |
Bs |
156 |
LIMN |
211 |
TALK |
266 |
Zu |
|
47 |
ss |
102 |
Bt |
157 |
LOAD |
212 |
TALK1 |
267 |
Zw |
|
48 |
tt |
103 |
Bu |
158 |
MC |
213 |
TEMP |
268 |
ZS |
|
49 |
uu |
104 |
Bw |
159 |
MC2 |
214 |
TH |
||
|
50 |
vv |
105 |
Bx |
160 |
MC4 |
215 |
THD |
||
|
51 |
ww |
106 |
BASE |
161 |
MC8 |
216 |
TWAIT |
||
|
52 |
xx |
107 |
BAUD |
162 |
MD |
217 |
UA |
||
|
53 |
yy |
108 |
BRKC |
163 |
MD50 |
218 |
UAA |
||
|
54 |
zz |
109 |
BRKENG |
164 |
MF0 |
219 |
UAI |
DLL for use with the OCS range in CSCAPE
Command
The drop down list contains all the commands that are supported. Commands that don’t send any data are set by writing any value to that register e.g “BRKG” is set by writing a value to it or else triggering it with a key.
Byte Array (ab[0-200])
The Index is the array position to be accessed. The value may be written / read to / from the array position pointed to by the index.
Word Array (aw[0-100])
The Index is the array position to be accessed. The value may be written / read to / from the array position pointed to by the index.
Long Array (al[0-50])
The Index is the array position to be accessed. The value may be written / read to / from the array position pointed to by the index.
Variable Load (VLD)/ Variable Store (VST)
These functions are used to implement the Variable Load (VLD) / Variable Store (VST) commands. The syntax form is VLD/VST (var, number). The variable may be any system or array variable. Choose the variable to store first and then write the number of variables to the local register in the OCS.
Variable Assignment ( var = U{Pin}I or var = U{Pin}A)
This Motor I/O function allows the user to assign digital or analog values of a I/O pin to a variable. In the command box the user selects both the variable and the pin. Writing the pin “x-y” in the pin box where “x” is the pin and “y” is either A or I for analog or digital. Then triggering or writing any value to this, completes the command.
RS-232 Serial Daisy Chain - MultiDrop Access
Multidrop access to different drive parameters is done using the ID in the Scan List. Select the ID to communicate with in the ID field of the data mapping section of the Protocol Configuration. Address the drives correctly before doing this. Writing a parameter to an ID that doesn’t exist, causes a corrupt or invalid response from the OCS.
Note: For RS-232 Multidrop mode, the OCS in ECHO_OFF Mode so it is necessary to set the ECHO ON for each drive.
Network Communication Errors
In order to access the Network statistics, user must assign the “Network status register” in network configuration. The table below gives the details of statistics.
| Number | Statistics | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Update interval exceeded count |
%Rx |
This register explains number of times that the actual transaction scan time to complete all transactions exceeded specified update interval. Generally used as an indicator that an excessive number of triggered transfers or failed communication retries are occurring that is lengthening the expected transaction scan time.
If the Update interval is set to zero (update as fast as possible), this 32-bit register alternately specifies the actual transaction scan time in mSec resolution. |
|
2 |
No response count |
%R(x+2) |
This register explains number of times that a device(s) did not respond to a transaction. This includes ALL failed transaction, not just those after the retry count is exceeded. |
|
3 |
Corrupt Response Count |
%R(x+4) |
This register explains number of times that a device(s) returned an invalid or failed response to a transaction. This includes ALL failed.
Transaction, not just those after the retry count is exceeded. |
|
4 |
Valid Response Count |
%R(x+6) |
This register explains total number of valid responses. |
Note: %Rx: 32-bit network status register configured in Network configuration. For example: %R500(501).
Device Communication Errors
| Error | Error Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
INVALID_BLOCK |
-203 |
Invalid size for data type. |
|
NO_RESPONSE_FROM_PLC |
-204 |
Timeout while waiting for remote node response. |
|
INVALID_RESPONSE_FROM_PLC |
-205 |
Corrupted response from remote node. |
|
INVALID_INITIALISATION |
-207 |
Internal Error - Unable to open port. |
Connection Details
Illustrations below show the various end-of-cable connectors required:
| 25-Pin D-Type Male | 10-Pin Weidmuller
Cage Clamp |
8-Pin RJ 45 Plug | 9-Pin DB Male |
|

|
|
|
| CN1 | CN1 | MJ1/MJ2 | Port 1 |
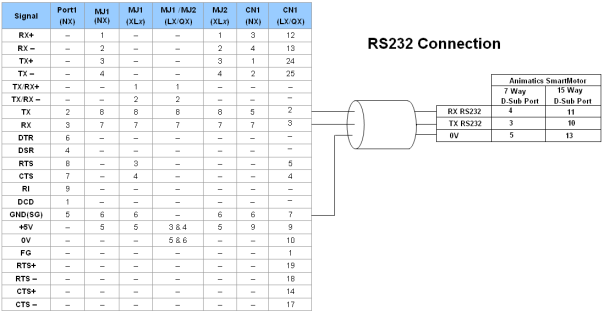
Port 1 — DB9 (Female at OCS end)
MJ1/MJ2 — RJ45 (Female at OCS end)
CN1 — 10-Pin Weidmuller Cage Clamp (Female at OCS end)
CN1 — DB25 (Female at OCS end)
Note:
-
Do not connect to unlisted pins.
-
Recommended Cable: Beldon 9503, twisted multipair, screened.
-
Connect the screens together at the shield / earth pin of the PLC.